Collapsible content
Benefits
Supports attention and emotional regulation for ADHD.
Promotes restful sleep and a sense of calm.
Enhances overall vitality and wellness with natural ingredients.
Why choose our solution?
Our products are formulated with thoughtfully selected, 100% natural ingredients, backed by science, and designed for optimal effectiveness. By choosing us, you’re supporting not just your well-being but also sustainable and eco-conscious practices.
Warning
Key Considerations
Supplements are not a replacement for medication or behavioral therapy but can complement these treatments.
Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement to avoid potential interactions or side effects.
Results vary widely; some supplements may show benefits in weeks, while others may take months or be ineffective.
By integrating supplements into a comprehensive treatment plan that includes nutrition, sleep hygiene, exercise, and behavioral strategies, families can better support ADHD management holistically.
For children, it's recommended to limit the dosage to no more than 1000mg per day to ensure safety while enhancing brain health and reducing ADHD symptoms.
ADHD
Prefrontal Cortex (PFC)
Prefrontal Cortex (PFC)
The PFC is crucial for attention, behavior regulation, and impulse control. In individuals with ADHD, this region often exhibits reduced activity and structural differences, leading to difficulties in maintaining attention and inhibiting impulsive actions.
Basal Ganglia:
Basal Ganglia:
This group of nuclei, including the caudate nucleus and putamen, is involved in motor control and executive functions. Structural and functional abnormalities in the basal ganglia have been observed in individuals with ADHD, potentially affecting attention and behavior regulation.
Neurotransmitter Imbalance
Neurotransmitter Imbalance
ADHD is associated with dysregulation of dopamine and norepinephrine systems. These neurotransmitters are vital for transmitting signals in the brain, and their imbalance can impair the PFC's ability to function properly, contributing to attention deficits.
Cerebellum
Cerebellum
Traditionally associated with motor control, the cerebellum also plays a role in cognitive processes. Studies have found structural differences in the cerebellum of those with ADHD, which may influence attention and executive function.
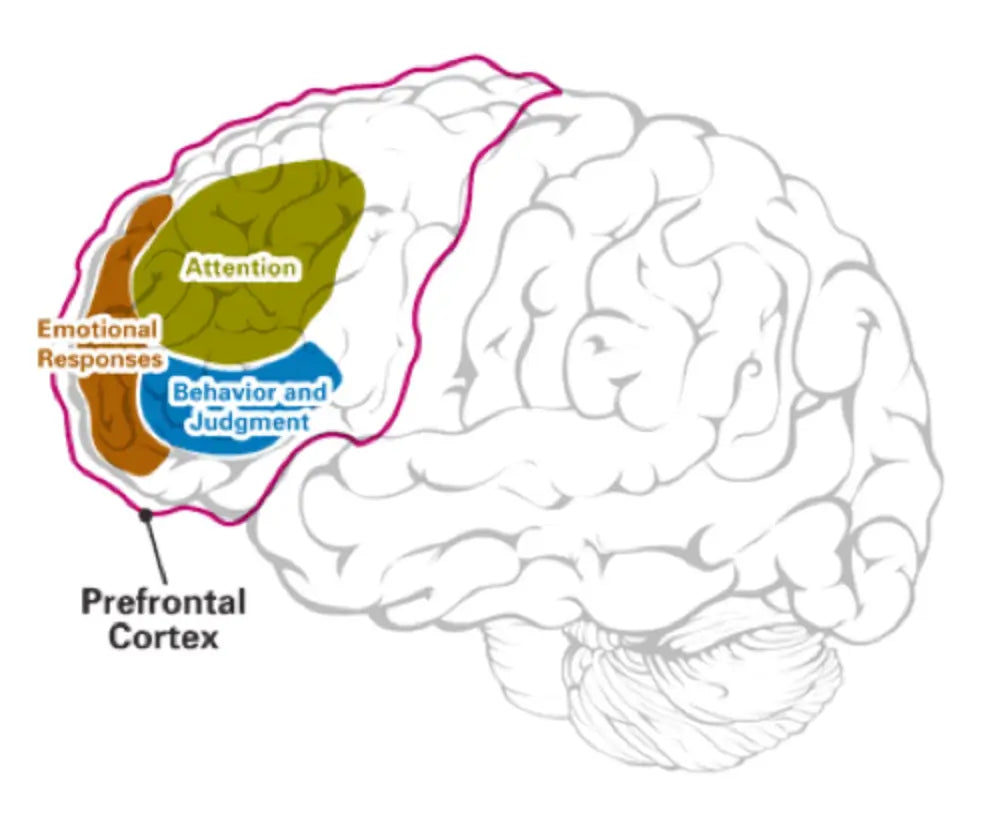
The PFC is crucial for attention, behavior regulation, and impulse control. In individuals with ADHD, this region often exhibits reduced activity and structural differences, leading to difficulties in maintaining attention and inhibiting impulsive actions.
This group of nuclei, including the caudate nucleus and putamen, is involved in motor control and executive functions. Structural and functional abnormalities in the basal ganglia have been observed in individuals with ADHD, potentially affecting attention and behavior regulation.
ADHD is associated with dysregulation of dopamine and norepinephrine systems. These neurotransmitters are vital for transmitting signals in the brain, and their imbalance can impair the PFC's ability to function properly, contributing to attention deficits.
Traditionally associated with motor control, the cerebellum also plays a role in cognitive processes. Studies have found structural differences in the cerebellum of those with ADHD, which may influence attention and executive function.
Video - ADHD explained
Benefits: Supports cognitive function, memory, and emotional balance by promoting neuronal health and reducing inflammation. Study here
Limitations: Effects are subtle compared to medications; therapeutic results may require long-term, consistent use.
Benefits: Moringa is a nutrient-rich plant, beneficial for ADHD and broader health. Its high calcium, protein, and iron content supports growth, development, and anemia treatment, while vitamins A and C exceed daily requirements, boosting immunity and recovery. It stabilizes blood sugar, promotes brain health through antioxidants, and reduces inflammation with compounds like quercetin. Omega-3s, magnesium, and zinc further aid brain function, concentration, and hyperactivity management.
Research: While studies directly linking Moringa to ADHD are scarce, its components are supported by evidence. For instance, omega-3 supplementation significantly manages ADHD symptoms, and Moringa’s dense nutritional profile enhances similar effects in growth, recovery, and cognitive health. here , here
Limitations: Despite its benefits, Moringa's use for ADHD lacks direct clinical validation. Variability in supplement quality and unregulated dosages limit its reliability. Integrating Moringa as part of ADHD management requires consultation with healthcare professionals.
-
Lion's Mane Mushroom natural extract
Regular price $35.00 USDRegular price Sale price $35.00 USDUnit price per3500 off -
Moringa Pure natural extract
Regular price $26.90 USDRegular price Sale price $26.90 USDUnit price per2690 off


